The Future of Payments 2034: How Tech Will Change the Way We Pay
Ten years ago, over 90% of transactions in Sub-Saharan Africa were cash-based payments. In 2024, digital payments have become widely accepted across Africa, reducing the need for cash payment for small and large-scale transactions. Other traditional payment methods, such as credit and debit cards are also starting to lose their usage for global payments and are being replaced by newer digital payment methods.
Technological advancements and the increasing demand for convenience, speed and security in payment have paved the way for innovations in paytech over the last decade. The constant rise of fintech in Africa, the improvement of payment infrastructure and the digitization of payments continue to destroy traditional systems and lead to the creation of newer payment services. This begs the question: what does the future hold for payment and how will technology change the way we pay in another decade?
This SeerBit article discusses some payment technologies and trends that will likely be mainstream in the next 10 years, specifically by the year 2034.
Digital Wallets
Digital wallets will likely become the primary mode of payment by 2034. According to the FIS Global payment report, by the year 2026, digital wallets are going to be the most used POS payment method, confirming the move away from traditional payment methods.
Digital wallets allow users to store multiple payment methods, such as credit/debit cards, bank accounts and even cryptocurrencies in one centralized platform, offering accessibility and convenience to users. With traditional banking infrastructure remaining limited across Africa and mobile phone penetration continuing to rise steadily, digital wallets are likely the future of payments in Africa.

Cryptocurrency
Blockchain - the technology behind cryptocurrencies - is a distributed ledger that keeps records, tracks and validates transactions securely and transparently. This makes it an ideal payment method, as it not only prevents fraud but also ensures accuracy. While it was only created in 2008, it has continued to grow so much that there are currently over 12000 cryptocurrencies.
The biggest appeal for cryptocurrency as a payment method is its decentralised nature, meaning it's not controlled by institutions or governments. This makes it an ideal payment method for an increasingly globalized world. However, many still see it as an investment opportunity rather than a payment method.
Till date, regulatory discussions and the fact that many still don't fully understand how cryptocurrency works have prevented its full adoption as a payment method. However, this is expected to change in a few years as internet users increase, the technology continues to trend and more people hold and use it.

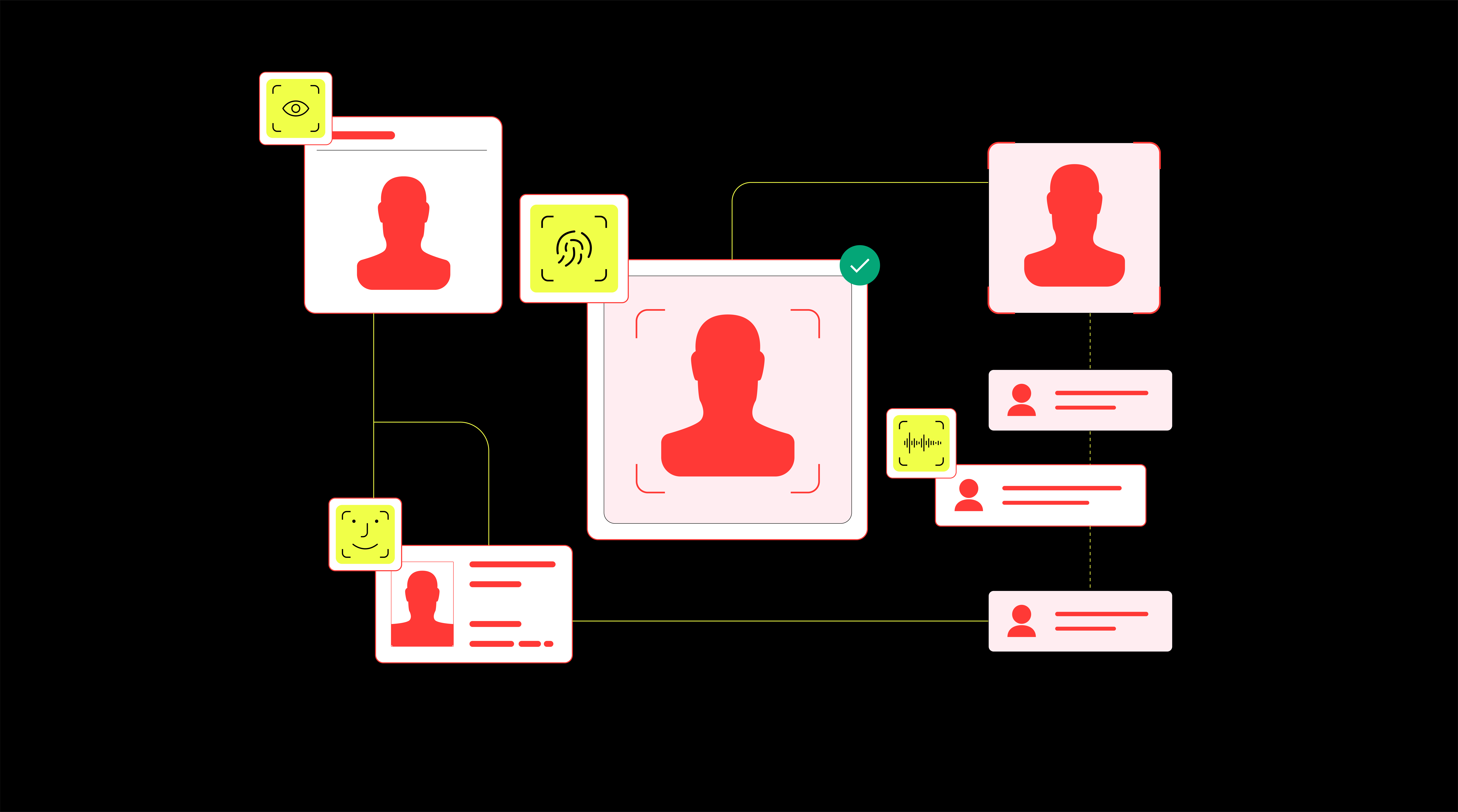
Biometric Payments
Biometric payments refers to a method of authentication and authorization of financial transactions that involves using unique physical or behavioural characteristics of individuals to verify their identity. This can include fingerprints, facial features, iris scans or voice recognition to identify users and authenticate payments. This offers a higher level of security compared to traditional methods such as passwords or PINs.
Since biometric identifiers are unique to each individual and difficult to replicate, they provide a robust layer of protection against unauthorized access and fraud. It reduces the risk of identity theft and fraud, as biometric data is unique to each individual and difficult to forge. This helps to instil trust and confidence among consumers, encouraging greater adoption of digital payment methods.
In a world where digital transactions are ubiquitous and payment security is a priority, adopting an authentication method that guarantees security is the way to go. So, we might see passwords and pins fade out, giving way to the mass adoption of biometric authentication.
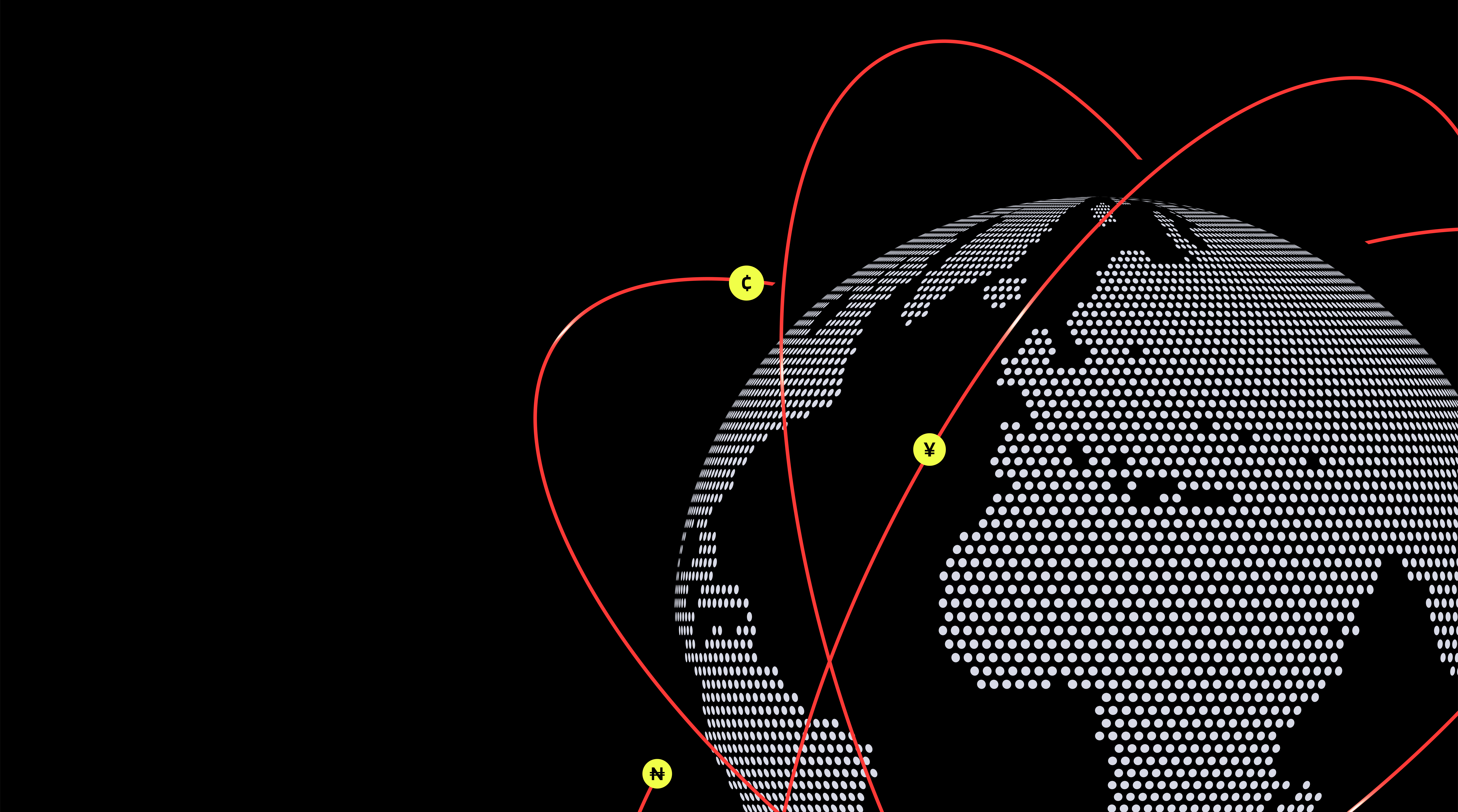
Cross Border Payment
Real-time cross-border payment is fast becoming the height that payment processors are trying to attain. Traditional banking systems, state-controlled currencies and market volatility currently contribute to the difficulties and inefficiencies in paying across borders. However, as payment processors not tied to traditional banks continue to grow and innovative solutions, such as blockchain and digital currencies become more commonplace, real-time borderless payments across Africa are becoming a reality.
According to Mordor Intelligence, there are already 70 countries across six continents, including Africa that support real-time payments and transaction volume is constantly rising. The expectation is that by 2034, real-time borderless payments will be commonplace.
Conclusion
The payment landscape in Nigeria and Africa at large is evolving steadily, propelled by seamless digital experiences and technological innovations. As such, technology will continue to impact the sector, with innovative systems such as biometric authentication and blockchain adoption expected to play a massive role in payments.